ESG Data Management and What You Need to Know
Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) are three central factors used to measure the sustainability and societal impact of a company. Adherence to ESG criteria, through ESG data collection and ESG data management, measures an organization’s contributions to sustainability and ethical practices in a way that provides transparency to the market, financial benefits to an organization and benchmarking for industry.
ESG is a response to increasing calls around the world for organizations to play a more significant role in creating a sustainable future while maintaining ethical behavior and contributing to the communities in which they operate. ESG data gathering and ESG data management are the measurable means that organizations apply to gauge their ESG performance and compliance. ESG is an implementation of the aspirations of the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, which contains 17 sustainable development goals (SDGs) according to the following categories:

*Note: some goals appear in more than one category.
The ability to successfully manage and report ESG is seen as an indication of strong corporate leadership and governance and defines an organization as an employer or partner of choice. In today's economy, organizations can also deliver higher business value and sustain competitive advantage by investing in ESG initiatives.
While ESG frameworks focus on reporting, the basis of that reporting will be the efficiency and awareness of organizational processes. ESG data management, integrated through environment, health and safety, supply chain and quality management processes, is important for ensuring ESG reporting reflects the operational excellence an organization has achieved.
An ESG score or rating is a measure of a company's performance on a wide range of environmental, social and governance risks. ESG ratings help investors identify companies that are lagging or leading in their industry, which may flag opportunities or risks not captured in conventional financial analysis.
Many regulatory frameworks now judge ESG considerations to be a fiduciary duty that investor organizations have to their clients, which means that organizations that don’t fulfill their ESG obligations could face legal and regulatory challenges.
What is ESG Data Management
The days of tracking data and processes in static Excel spreadsheets are over. Corporations that are at the forefront of ESG reporting use online, real-time ESG data management software to manage their compliance obligations and beyond. From an investor standpoint, recordkeeping provided through a foundation built upon ESG data management is an important component of demonstrating that ESG goals are being met. But what solutions are available to ensure that a corporation is incorporating ESG into daily workflows? Below is a quick summary for specific areas of ESG.
Environmental
EHS data management is key to accurate reporting of greenhouse gas (GHG), generating compliance reports and the ability to keep track of product waste from generation to disposition. The Intelex Assets and Compliance Tracking System (ACTS), for example, is a web-based environmental management information system (EMIS) used for collecting data on a variety of environmental mediums including air, water and waste.
Social
The social element of ESG requires organizations to consider the safety and well-being of both their workers and the communities of which they are a part. From the perspective of ESG data management, an occupational health and safety management system (OHSMS) is critical for collecting ESG management data from leading and lagging indicators to help prevent worker injury and for encouraging strong safety culture across the organization.
Governance
ESG can also assist in the effort to become a better corporate citizen. Keeping adequate records through ESG data management and other technologies for items such as accounting and board meetings is just a start. To meet these obligations, a document management system that allows organizations to centralize and standardize critical documents in an automated workflow is crucial. Corporations should think broadly about how to use technologies such as ESG data management and even third-party tools to manage corporate governance. Governance in this context also means giving back to the local community. The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal 17 specifically mentions the role of partnerships as key to reaching out to remote parts of the community, allowing corporations to leverage strengths itself does not have, particularly in relation to technology.
Check out the Intelex Insight Report, What Does ESG Have to Do with Me? How Businesses Can Harness Technology in the Fight for Sustainability, for more information.
The Importance of ESG Data
ESG is about more than simply good intentions and strong marketing campaigns. Instead, data management that includes collection, analysis and reporting are the most important components of a strong ESG program. ESG efforts must be quantifiable, measurable and strategic, not simply aspirational talking points.
However, not all data are good data. In the rush to be part of the ESG data management, data collection and the analytics revolution, many organizations haphazardly collect data without distinguishing between high-quality data and low-quality data. Data quality refers to whether or not the data are fit for purpose and meet the requirements for analysis. Poor quality data result from such things as errors in manual entry, inefficient processes, aging data that becomes irrelevant, lack of common data standards and poor data governance.
Poor quality data can have significant negative impacts on the credibility of ESG initiatives, including poor ratings from ESG ratings agencies, negative brand impact and increased organizational risk. The table below shows some of the most common and important dimensions of data quality in the context of ESG data management.
Get the Intelex Insight Report, ESG Data: What Should You Collect and Why, for more information.
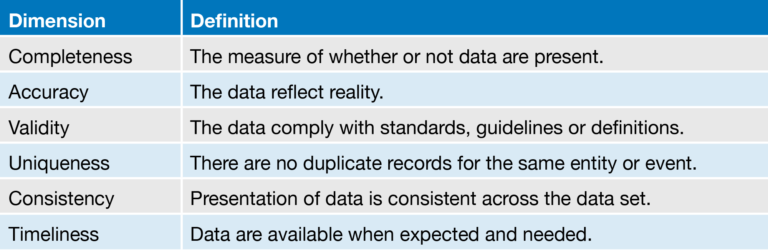
Metrics and Disclosures
In January 2020, the International Business Council (IBC), an organization within the World Economic Forum, launched an initiative to define common metrics for ESG reporting. The goal of this project was to ensure that organizations have a clear and consistent approach to measuring their ESG initiatives and providing value to stakeholders along the entire value chain.
IBC created a set of core and expanded Stakeholder Capitalism Metrics that align with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals. These 21 core metrics focus on internal activities that are probably already being collected by many organizations. The 34 expanded metrics are less likely to be collected at present and extend along the entire value chain. Together, these metrics can help organizations better understand how to determine the shape and scope of their ESG initiatives
The Intersection of ESG and EHS
Most EHS professionals would rightly declare the work they’ve been doing has aligned with many ESG principles all along (See the Intelex Insight Report: What Every EHS Leader Should Know about ESG). However, some in senior business leadership were too often not interested in EHS concerns unless there was a significant miss in compliance and targets, and they typically only looked at a few metrics to measure success. The outline of ESG gives EHS practitioners a platform to be a business partner that's not simply judged from a cost-avoidance function, but as a real partner in the business.
Data that’s currently being gathered by EHS systems, such as emissions tracking, climate change information and health and safety information, could likewise feed the “social” part of ESG data management and ESG reporting. EHS elements are tied to sustainability reporting, which has been around for decades. If you consider what companies report on for sustainability, a considerable amount of it has EHS elements. ESG is a new flavor of sustainability reporting. The chart below shows how ESG data management and reporting align with EHS data management and collection efforts.
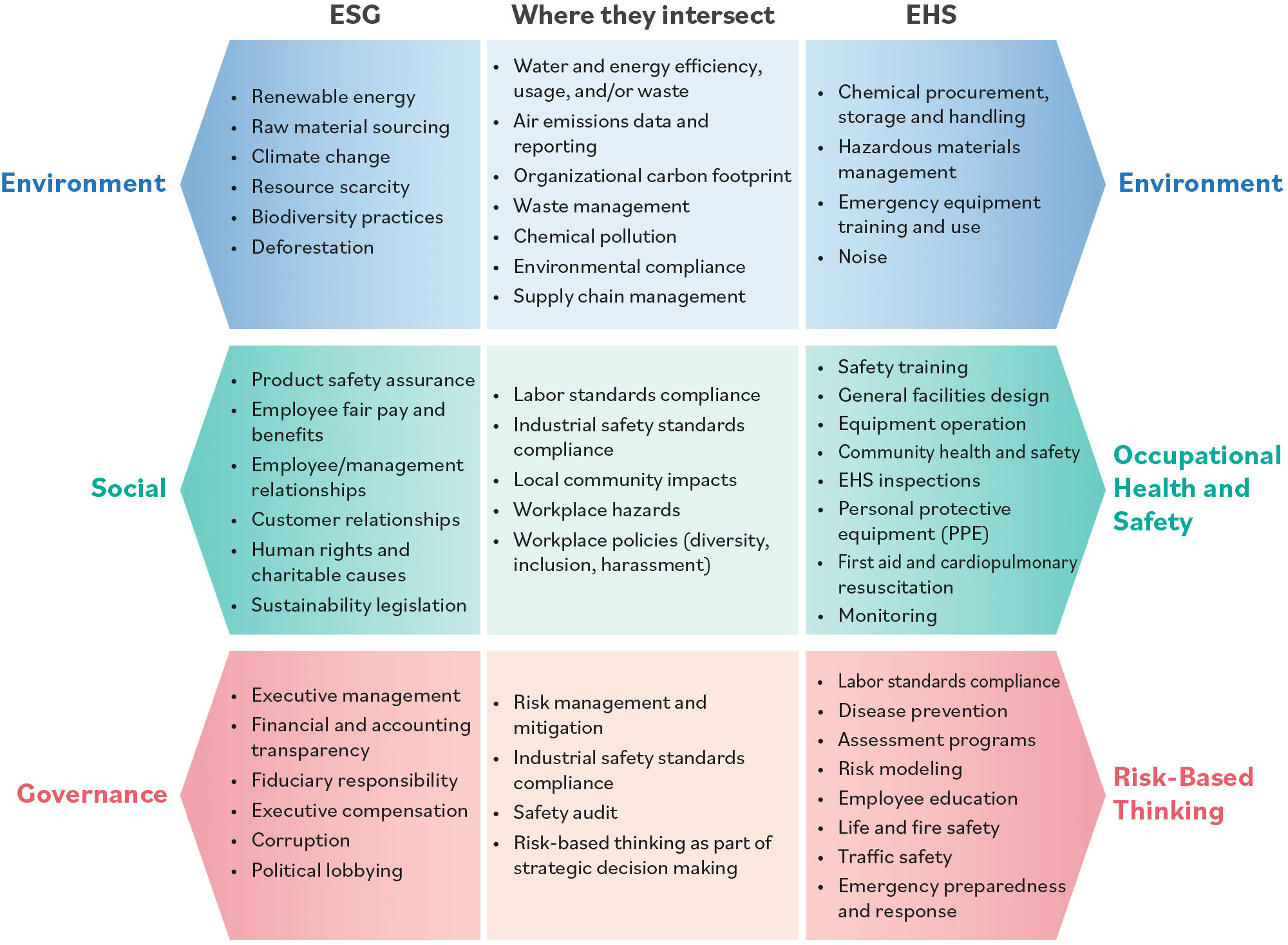
How Intelex Supports ESG Data Management and Collection
ESG data management solutions are the engines that drive efforts by organizations to abide by ESG principles that consider non-financial elements when measuring material risks and opportunities. While applications for measuring internal ESG data within the organization will continue to be critical, new artificial intelligence (AI)-based applications are providing innovative approaches to monitoring the external landscape to improve overall ESG data management, risk management, annual reporting and Board oversight.
Intelex is a cloud-based, software-as-a-service (SaaS) platform that allows organizations to monitor, measure and improve environment, health, safety and quality (EHSQ) processes. Integrated management systems for EHSQ built on Intelex can use applications like Assets and Compliance Tracking System (ACTS) and Sustainability Performance Indicators (SPIs) to collect data on air, water and waste and to report on sustainability initiatives across the organization, while other applications for health, safety and quality can support such critical activities as leading and lagging indicators, supply chain management, risk and nonconformances. As a result, organizations can reduce risk and ensure compliance for all of their EHSQ obligations while fulfilling their obligations to ESG data management and reporting.
Before Intelex can measure and improve internal processes, the organization must recognize what its obligations, risks and opportunities are by understanding key competitive, regulatory and reputational drivers. While this has previously proven overwhelming for many organizations, AI applications are helping to make this a more common reality.
Intelex uses Compliance Automation Software to augment its AI capabilities and put more analytic power in the hands of organizational leadership. Compliance Automation Software uses AI and machine learning (ML) to help organizations transform the way they manage regulatory compliance. It also uses Optical Character Recognition (OCR), Natural Language Processing (NLP) along with AI to quickly analyze complex requirements such as permits, standards, regulations, consent decrees, policies, guidance documents and more.
From this process, Compliance Automation Software produces a detailed and structured document in .xlsx or .csv, or via APIs, that can be used as an input to a management system that highlights the important elements organizations need to know to meet their obligations. Compliance Automation Software output provides the basis for what Intelex needs to monitor, measure and improve to facilitate compliance.
 1 877 932 3747
1 877 932 3747




